Why Do We Study Ice?
Why Do We Study Ice?
Discover why we study ice and how this research benefits Earth.

We fly our DC-8 aircraft very low over Antarctica as part of Operation IceBridge – a mission that’s conducting the largest-ever airborne survey of Earth’s polar ice.

Records show that 2015 was the warmest year on record, and this heat affects the Arctic and Antarctica – areas that serve as a kind of air conditioner for Earth and hold an enormous of water.

IceBridge flies over both Greenland and Antarctica to measure how the ice in these areas is changing, in part because of rising average global temperatures.
IceBridge’s data has shown that most of Antarctica’s ice loss is occurring in the western region. All that melting ice flows into the ocean, contributing to sea level rise.

IceBridge has been flying the same routes since the mission began in 2009. Data from the flights help scientists better measure year-to-year changes.

IceBridge carries the most sophisticated snow and ice instruments ever flown. Its main instrument is called the Airborne Topographic Mapper, or ATM.The ATM laser measure changes in the height of the ice surface by measuring the time it takes for laser light to bounce off the ice and return to the plane – ultimately mapping ice in great detail, like in this image of Antarctica’s Crane Glacier.

For the sake of the laser, IceBridge planes have to fly very low over the surface of snow and ice, sometimes as low as 1,000 feet above the ground. For comparison, commercial flights usually stay around 30,000 feet! Two pilots and a flight enginner manage the many details involved in each 10- to 12-hour flight.

One of the scientific radars that fly aboard IceBridge helped the British Antarctic Survey create this view of what Antarctica would look like without any ice.

IceBridge also studies gravity using a very sensitive instrument that can measure minuscule gravitational changes, allowing scientists to map the ocean cavities underneath the ice edges of Antarctica. This data is essential for understanding how the ice and the ocean interact. The instrument’s detectors are very sensitive to cold, so we bundle it up to keep it warm!

Though the ice sheet of Antarctica is two miles thick in places, the ice still “flows” – faster in some places and slower in others. IceBridge data helps us track how much glaciers change from year-to-year.

Why do we call this mission IceBridge? It is bridging the gap between our Ice, Cloud and Land Elevation Satellite, or ICESat – which gathered data from 2003 to 2009 – and ICESat-2, which will launch in 2018.

Learn more about our IceBridge mission here: www.nasa.gov/icebridge and about all of our ice missions on Twitter at @NASA_Ice.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from F-taser-blog and Others
Tudeww
Hunting for Organic Molecules on Mars

Did Mars once have life? To help answer that question, an international team of scientists created an incredibly powerful miniature chemistry laboratory, set to ride on the next Mars rover.

The instrument, called the Mars Organic Molecule Analyzer Mass Spectrometer (MOMA-MS), will form a key part of the ExoMars Rover, a joint mission between the European Space Agency (ESA) and Roscosmos. A mass spectrometer is crucial to send to Mars because it reveals the elements that can be found there. A Martian mass spectrometer takes a sample, typically of powdered rock, and distinguishes the different elements in the sample based on their mass.

After 8 years of designing, building, and testing, NASA scientists and engineers from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center said goodbye to their tiny chemistry lab and shipped it to Italy in a big pink box. Building a tiny instrument capable of conducting chemical analysis is difficult in any setting, but designing one that has to launch on a huge rocket, fly through the vacuum of space, and then operate on a planet with entirely different pressure and temperature systems? That’s herculean. And once on Mars, MOMA has a very important job to do. NASA Goddard Center Director Chris Scolese said, “This is the first intended life-detecting instrument that we have sent to Mars since Viking.”

The MOMA instrument will be capable of detecting a wide variety of organic molecules. Organic compounds are commonly associated with life, although they can be created by non-biological processes as well. Organic molecules contain carbon and hydrogen, and can include oxygen, nitrogen, and other elements.

To find these molecules on Mars, the MOMA team had to take instruments that would normally occupy a couple of workbenches in a chemistry lab and shrink them down to roughly the size of a toaster oven so they would be practical to install on a rover.

MOMA-MS, the mass spectrometer on the ExoMars rover, will build on the accomplishments from the Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM), an instrument suite on the Curiosity rover that includes a mass spectrometer. SAM collects and analyzes samples from just below the surface of Mars while ExoMars will be the first to explore deep beneath the surface, with a drill capable of taking samples from as deep as two meters (over six feet). This is important because Mars’s thin atmosphere and spotty magnetic field offer little protection from space radiation, which can gradually destroy organic molecules exposed on the surface. However, Martian sediment is an effective shield, and the team expects to find greater abundances of organic molecules in samples from beneath the surface.

On completion of the instrument, MOMA Project Scientist Will Brinckerhoff praised his colleagues, telling them, “You have had the right balance of skepticism, optimism, and ambition. Seeing this come together has made me want to do my best.”
In addition to the launch of the ESA and Roscosmos ExoMars Rover, in 2020, NASA plans to launch the Mars 2020 Rover, to search for signs of past microbial life. We are all looking forward to seeing what these two missions will find when they arrive on our neighboring planet.
Learn more about MOMA HERE.
Learn more about ExoMars HERE.
Follow @NASASolarSystem on Twitter for more about our missions to other planets.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
"don't blame gravity for falling in love"
Albert eienstine
Check that out!
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Ready for a free show? Here’s our guide to the brightest shows on Earth for 2017–meteor showers! And, there’s no telescope required.
The sky may not be falling, but it can certainly seem that way during a meteor shower. Shooting stars, as meteors are sometimes called occur when rock and debris in space fall through the Earth’s atmosphere, leaving a bright trail as they are heated to incandescence by friction with the air. Sometimes the number of meteors in the sky increases dramatically, becoming meteor showers. Some showers occur annually or at regular intervals as the Earth passes through the trail of dusty debris left by a comet. Here’s a guide to the top meteor showers expected in 2017.

1. Quadrantids, January 3-4
At its peak this shower will have about 40 meteors per hour. The parent comet is 2003 EH1, which was discovered in 2003. First quarter moon sets after midnight and meteors radiate from the constellation Bootes.

2. Eta Aquarids, May 6-7
This shower will have up to 60 meteors per hour at its peak and is produced by dust particles left behind by comet Halley, which has been known and observed since ancient times. The shower runs annually from April 19 to May 28. The waxing gibbous moon will block out many of the fainter meteors this year. Meteors will radiate from the constellation Aquarius.

3. Perseids, August 12-13
The annual Perseid shower will have up to 60 meteors per hour at its peak. It is produced by comet Swift-Tuttle. The Perseids are famous for producing a large number of bright meteors. The shower runs annually from July 17 to August 24. The waning gibbous moon will block out many of the fainter meteors this year, but the Perseids are so bright and numerous that it should still be a good show. Meteors will radiate from the constellation Perseus.

4. Draconids, October 7
This is a minor shower that will produce only about 10 meteors per hour. It is produced by dust grains left behind by comet 21P Giacobini-Zinner, which was first discovered in 1900. The Draconids is an unusual shower in that the best viewing is in the early evening instead of early morning like most other showers. The shower runs annually from October 6-10 and peaks this year on the the night of the 7th. Unfortunately, the nearly full moon will block all but the brightest meteors this year. If you are extremely patient, you may be able to catch a few good ones. Meteors will radiate from the constellation Draco.

5. Geminids, December 13-14
The Geminids may be the best shower, producing up to 120 meteors per hour at its peak. It is produced by debris left behind by an asteroid known as 3200 Phaethon, which was discovered in 1982. The shower runs annually from December 7-17. The waning crescent moon will be no match for the Geminids this year. The skies should still be dark enough for an excellent show. Meteors will radiate from the constellation Gemini, but can appear anywhere in the sky.
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
LETS DO IT TOGETHER NASA :)
Mission Possible: Redirecting an Asteroid
As part of our Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM), we plan to send a robotic spacecraft to an asteroid tens of millions of miles away from Earth, capture a multi-ton boulder and bring it to an orbit near the moon for future crew exploration.
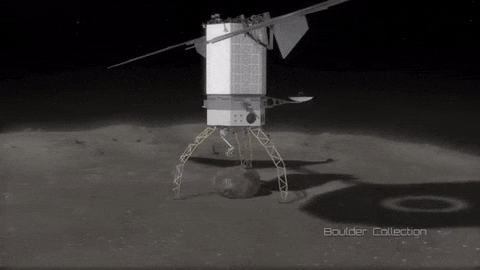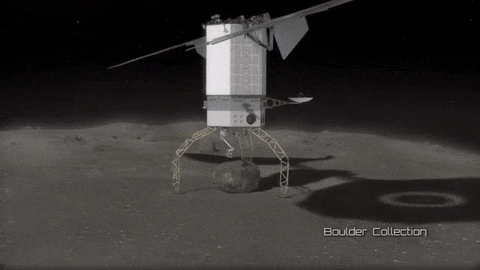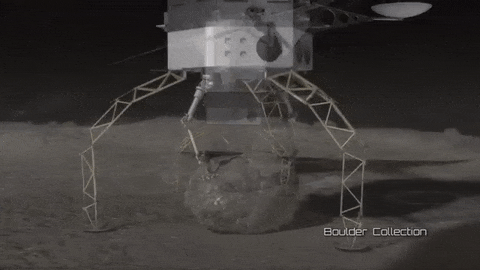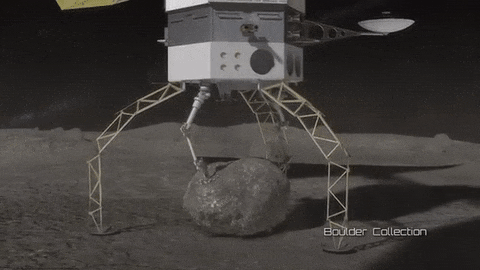
This mission to visit a large near-Earth asteroid is part of our plan to advance the new technologies and spaceflight experience needed for a human mission to the Martian system in the 2030s.
How exactly will it work?
The robotic spacecraft, powered by the most advanced solar electric propulsion system, will travel for about 18 months to the target asteroid.

After the spacecraft arrives and the multi-ton boulder is collected from the surface, the spacecraft will hover near the asteroid to create a gravitational attraction that will slightly change the asteroid’s trajectory.

After the enhanced gravity tractor demonstration is compete, the robotic vehicle will deliver the boulder into a stable orbit near the moon. During the transit, the boulder will be further imaged and studied by the spacecraft.

Astronauts aboard the Orion spacecraft will launch on the Space Launch System rocket to explore the returned boulder.

Orion will dock with the robotic vehicle that still has the boulder in its grasp.

While docked, two crew members on spacewalks will explore the boulder and collect samples to bring back to Earth for further study.

The astronauts and collected samples will return to Earth in the Orion spacecraft.
How will ARM help us send humans to Mars in the 2030s?

This mission will demonstrate future Mars-level exploration missions closer to home and will fly a mission with technologies and real life operational constraints that we’ll encounter on the way to the Red Planet. A few of the capabilities it will help us test include:
Solar Electric Propulsion – Using advanced Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) technologies is an important part of future missions to send larger payloads into deep space and to the Mars system. Unlike chemical propulsion, which uses combustion and a nozzle to generate thrust, SEP uses electricity from solar arrays to create electromagnetic fields to accelerate and expel charged atoms (ions) to create a very low thrust with a very efficient use of propellant.
Trajectory and Navigation – When we move the massive asteroid boulder using low-thrust propulsion and leveraging the gravity fields of Earth and the moon, we’ll validate critical technologies for the future Mars missions.
Advances in Spacesuits – Spacesuits designed to operate in deep space and for the Mars surface will require upgrades to the portable life support system (PLSS). We are working on advanced PLSS that will protect astronauts on Mars or in deep space by improving carbon dioxide removal, humidity control and oxygen regulation. We are also improving mobility by evaluating advances in gloves to improve thermal capacity and dexterity.
Sample Collection and Containment Techniques – This experience will help us prepare to return samples from Mars through the development of new techniques for safe sample collection and containment. These techniques will ensure that humans do not contaminate the samples with microbes from Earth, while protecting our planet from any potential hazards in the samples that are returned.
Rendezvous and Docking Capabilities – Future human missions to Mars will require new capabilities to rendezvous and dock spacecraft in deep space. We will advance the current system we’ve developed with the international partners aboard the International Space Station.
Moving from spaceflight a couple hundred miles off Earth to the proving ground environment (40,000 miles beyond the moon) will allow us to start accumulating experience farther than humans have ever traveled in space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
'Make a green change' series posts
Yo there, I’m releasing a new series post which is being post on to F-taser. Let’s get to the point, yeah I’m talking about how we all together can make a simple green change.everyday we already have two to three hours of free time, of you everyday consume only just twenty minutes for this ‘go green’ projects, we could make a very great difference and we could relax a lot with this green environment. Yes you could really feel a great difference.while breathing this plant-purified air you could get that green energy. In the following post will post some how-to projects to go green… Bye. And happy Christmas everyone
You know now a clash is going on between India and Pak, and let us pray for the soilders.. Saint Mother Teresa said "If we have no peace, It is beacause we have forgotten that we belong to each other"..
6 Tiny Satellites That Are Changing How We See Earth

HARP: Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter
What’s better than taking a picture of a cloud to figure out its size and shape? Taking a bunch of pictures all around it. That way you get a three-dimensional view without having to worry about missing something. The HARP CubeSat is going to do just that: make observations of cloud droplets and tiny airborne particles like soot and dust with a modified camera lens from multiple angles. This will give us a full rendering of what’s going on inside the clouds, specifically, how those airborne particles act as “seeds” for water vapor to condense on and form cloud droplets. Since so many of those particles are in the air as a result of man-made pollution, we want to understand how they may be affecting clouds, weather and climate.

RAVAN: Radiometer Assessment using Vertically Aligned Nanotubes
Anyone who’s worn a black shirt on a summer day knows how much sunlight and heat it absorbs. The RAVAN 3-unit CubeSat, however, carries “blacker than black” technology – carbon nanotubes set up like a bundle of drinking straws that suck up nearly all the sunlight and energy that reach them to the point that your black shirt seems merely dark grey in comparison. Flying in low Earth orbit, RAVAN’s super sensitive instrument will detect tiny changes in the amount of sunlight and energy passing into and out of the top of the atmosphere. The amount of energy passing through the top of the atmosphere is where the net accounting of Earth’s energy budget happens – one of the major measurements we need in order to understand the effects of greenhouse gases on global warming and climate change.

MiRaTA: Microwave Radiometer Technology Acceleration
That long skinny piece coming out of the bottom right side under the solar panel? That’s a measuring tape. It’s doubling as a communications antenna on the MiRaTA CubeSat that will be a mini-weather station in space. This 3-unit, shoe box-sized satellite is testing out new, miniaturized technology to measure temperature, water vapor, and cloud ice in the atmosphere. They’ll be tracking major storms, including hurricanes, as well as everyday weather. If this test flight is successful, the new, smaller technology will likely be incorporated into major – large – weather satellite missions in the future that are part of our national infrastructure.

IceCube
The aptly named IceCube will measure – you guessed it – ice in our atmosphere. Unlike the droplets that make up rain, ice is one of the harder things to measure from space. IceCube is a 3-unit CubeSat about the size of a loaf of bread outfitted with a new high-frequency microwave radiometer, an instrument that measures naturally occurring radiation emitted by stuff in the atmosphere – cloud droplets, rain, and the ice particles at the tops of clouds. This will be the first space test of the new microwave radiometer that has to balance its tiny size and low power with being sensitive enough to detect cloud ice.

CYGNSS: Cyclone, Global Navigation Satellite System
What do GPS signals do when they’re not talking to your phone? A lot of them are just bouncing harmlessly off the planet’s surface – a fact that the CYGNSS mission is taking advantage of to measure wind speed over the ocean. Eight identical small satellites, each about the size of a microwave oven, flying in formation carry custom modified GPS receivers pointed at the oceans. When the water is smooth – not windy – the GPS signals reflect back uniformly, like the moon on a pond reflected as if in a mirror. When the water is choppy – windy – the signals reflect back in in the same direction but distorted, like the moon reflection on a choppy pond being distorted by ripples. Flying eight satellites in formation means the CYGNSS mission can measure wind speed across more of the ocean at once, which will help with understanding tropical storms and hurricanes.

TROPICS: Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats
An important way to improve forecasts of hurricane and tropical cyclone intensity is to see what’s going on inside and around them while they’re happening. That’s the goal of the TROPICS mission, 12 CubeSats that will fly in formation to track the temperature and humidity of storm environments. The TROPICS CubeSats will get very frequent measurements, similar to X-rays, that cut through the overall cloud-cover so we can see the storm’s underlying structure. The storm structures known as the eyewall – tall clouds, wind and rain around the eye – and rainbands – the rainy parts of the spiral arms – give us clues about whether a storm is primed to intensify into a category 4 or 5 storm, something everyone in their path needs to know.
Learn more the world of small satellites at: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
That's a good nature living idea ; green idea😇

An Indian company created shopping bags that are 100% natural, biodegradable, and edible. It took 4 years to develop the bags, which are made of potato, tapioca, corn, starches, and vegetable oils. Though slightly more expensive than plastic, the bags break down quickly, dissolve completely, and become a safe food source for animals rather than a choking hazard. Source
-
 green-guerrilla-larix reblogged this · 1 year ago
green-guerrilla-larix reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 larices liked this · 1 year ago
larices liked this · 1 year ago -
 stratobomber75 liked this · 5 years ago
stratobomber75 liked this · 5 years ago -
 dc-6engineer reblogged this · 5 years ago
dc-6engineer reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 goavi8tor liked this · 5 years ago
goavi8tor liked this · 5 years ago -
 dc-8mechanic reblogged this · 6 years ago
dc-8mechanic reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 studebakerman liked this · 6 years ago
studebakerman liked this · 6 years ago -
 supersarcosmic liked this · 7 years ago
supersarcosmic liked this · 7 years ago -
 buffyandhenrietta reblogged this · 7 years ago
buffyandhenrietta reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 destroyedeverythingandlaughed24 liked this · 8 years ago
destroyedeverythingandlaughed24 liked this · 8 years ago -
 stantherube liked this · 8 years ago
stantherube liked this · 8 years ago -
 geralmoncada reblogged this · 8 years ago
geralmoncada reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 keenwanderer reblogged this · 8 years ago
keenwanderer reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 imamplavitepih-blog liked this · 8 years ago
imamplavitepih-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 thenortherner31 liked this · 8 years ago
thenortherner31 liked this · 8 years ago -
 alicerobertstext reblogged this · 8 years ago
alicerobertstext reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 turalahmadsoy liked this · 8 years ago
turalahmadsoy liked this · 8 years ago -
 rottenlittleboys reblogged this · 8 years ago
rottenlittleboys reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 safyresky reblogged this · 8 years ago
safyresky reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 meterologistalien reblogged this · 8 years ago
meterologistalien reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 aerokiinesis liked this · 8 years ago
aerokiinesis liked this · 8 years ago -
 freeinstagramfollows-blog liked this · 8 years ago
freeinstagramfollows-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 54r4d145-blog liked this · 8 years ago
54r4d145-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 fuzzyangrybird reblogged this · 8 years ago
fuzzyangrybird reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 micos77 reblogged this · 8 years ago
micos77 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 121mcv reblogged this · 8 years ago
121mcv reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 121mcv liked this · 8 years ago
121mcv liked this · 8 years ago -
 eikosi8 liked this · 8 years ago
eikosi8 liked this · 8 years ago
