Latest Posts by science-child - Page 3
A small question:
Would anybody want me to do lessons? Like if you send in an ask like 'Hey, what do you know abt *science topic*?' I could do some research and make it a post with links and videos? (Like my Gravitational Waves in the Space-Time Continuum post [link below, and pinned to my acct])

Would anybody send in asks???
reiterate the science they hate...
Bill Nye said wear a fucking mask!!!
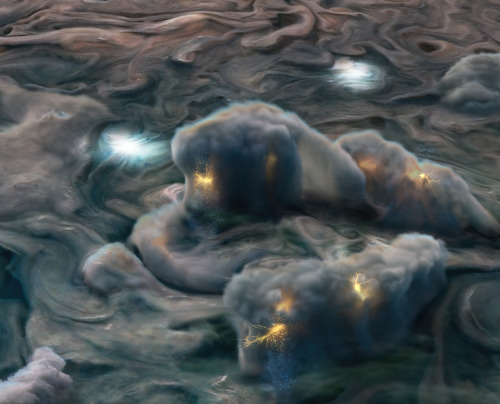

New results from our Juno mission suggest the planet is home to “shallow lightning.” An unexpected form of electrical discharge, shallow lightning comes from a unique ammonia-water solution.
It was previously thought that lightning on Jupiter was similar to Earth, forming only in thunderstorms where water exists in all its phases – ice, liquid, and gas. But flashes observed at altitudes too cold for pure liquid water to exist told a different story. This illustration uses data obtained by the mission to show what these high-altitude electrical storms look like.
Understanding the inner workings of Jupiter allows us to develop theories about atmospheres on other planets and exoplanets!
Illustration Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Gerald Eichstädt/Heidi N. Becker/Koji Kuramura
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com




Namaste Asexuals,
On this World Suicide Prevention Day We would request you to reach out to someone who will understand your Sexual orientation, will listen you out and won't judge you.
You can always ask for help - it might not fix things, but it can really make a difference for the better.
You can write us on :- indianasexuals@gmail.com
.
You can reach out to us on:-
-www.twitter.com/Indianasexuals
-Instagram.com/Indianasexuals
Source of survey :-
www.unicornmarch.org

Got a question about black holes? Let’s get to the bottom of these odd phenomena. Ask our black hole expert anything!
Black holes are mystifying yet terrifying cosmic phenomena. Unfortunately, people have a lot of ideas about them that are more science fiction than science. Don’t worry! Our black hole expert, Jeremy Schnittman, will be answering your your questions in an Answer Time session on Wednesday, October 2 from 3pm - 4 pm ET here on NASA’s Tumblr! Make sure to ask your question now by visiting http://nasa.tumblr.com/ask!
Jeremy joined the Astrophysics Science Division at our Goddard Space Flight Center in 2010 following postdoctoral fellowships at the University of Maryland and Johns Hopkins University. His research interests include theoretical and computational modeling of black hole accretion flows, X-ray polarimetry, black hole binaries, gravitational wave sources, gravitational microlensing, dark matter annihilation, planetary dynamics, resonance dynamics and exoplanet atmospheres. He has been described as a “general-purpose astrophysics theorist,” which he regards as quite a compliment.

Fun Fact: The computer code Jeremy used to make the black hole animations we featured last week is called “Pandurata,” after a species of black orchid from Sumatra. The name pays homage to the laser fusion lab at the University of Rochester where Jeremy worked as a high school student and wrote his first computer code, “Buttercup.” All the simulation codes at the lab are named after flowers.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Are You Up to the Task of Navigating Space with NASA?

We’re committed to exploration and discovery, journeying to the Moon, Mars, and beyond. But how do we guide our missions on their voyage among the stars? Navigation engineers lead the way!
Using complex mathematical formulas, navigation experts calculate where our spacecraft are and where they’re headed. No matter the destination, navigating the stars is a complicated challenge that faces all our missions. But, we think you’re up to the task!
Our space navigation workbook lets you explore the techniques and mathematical concepts used by navigation engineers. The book delves into groundbreaking navigation innovations like miniaturized atomic clocks, autonomous navigation technologies, using GPS signals at the Moon, and guiding missions through the solar system with X-ray emissions from pulsars — a type of neutron star. It also introduces you to experts working with NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation program at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
If you’re a high schooler who dreams of guiding a rover across the rocky surface of Mars or planning the trajectory of an observer swinging around Venus en route to the Sun, this workbook is for you! Download it today and start your adventure with NASA: https://go.nasa.gov/3i7Pzqr







hey everyone! i’m a peer tutor at my university and i wanted to share some study strategies that i’ve found really helpful in my stem/content-heavy courses. please feel free to share yours with me as well!
(image descriptions under the cut)
Keep reading
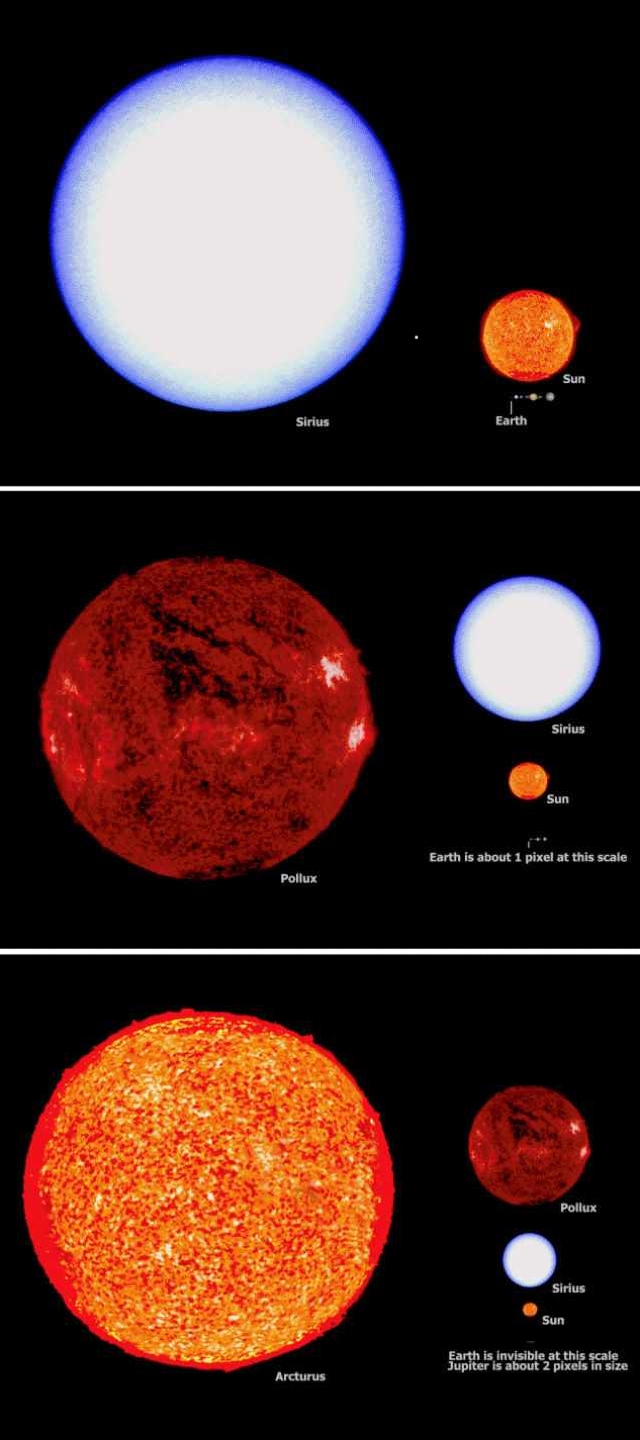
That's true with stars. We can never see stars or planets in the 'now' bc it took the light we are seeing time to get to us.
Even the sunlight takes 8 minutes to travel from the sun to earth, so if the sun exploded, we wouldn't know for 8 minutes.
In 2015, LIGO detected some gravitational waves from something that happened 1.3 billion years ago, in the constellation, Hydra. If you were on Hydra looking at Earth rn, you'd be seeing Earth from 1.3 billion years ago. 1.3 billion years ago, we were in the Mesoproterozoic Era here on earth. Life was just beginning to develop into multi-cellular organisms.
In conclusion: yes
wait i was in a tiktok comment section for something abt space and im no scientist obviously, but what if the reason we haven't found proof of life in space yet is because light takes time to travel from there to earth. like we arent seeing what's currently happening up there just what was happening way in the past.
"The vast sun-clusters' gather'd blaze, world-isles in lonely skies, whole heavens within themselves, our brief humanities."
-Alfred Lord Tennyson, 1885
"Equipped with his five senses, man explores the universe around him and calls the adventure science."
-Edwin P. Hubble

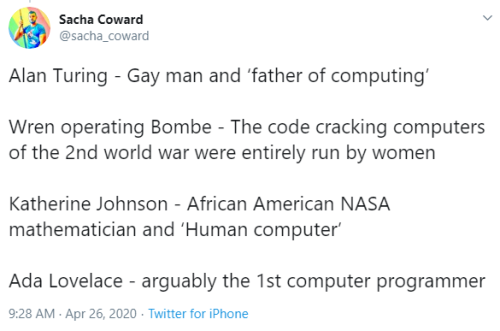


“I always remember having this fight with a random dude who claimed that ‘straight white men’ were the only true innovators. His prime example for this was the computer… the computer… THE COMPUTER!!! THE COM-PU-TER!!!
Alan Turing - Gay man and ‘father of computing’ Wren operating Bombe - The code cracking computers of the 2nd world war were entirely run by women Katherine Johnson - African American NASA mathematician and ‘Human computer’ Ada Lovelace - arguably the 1st computer programmer”
- Sacha Coward
Also Margaret Hamilton - NASA computer scientist who put the first man on the moon - an as-yet-unmatched feet of software engineering, here pictured beside the full source of that computer programme. #myhero
Grace Hopper - the woman that coined the term “bug”
- @robinlayfield
“If you read the history of the development of chemistry and particularly of physics, you will see that even such exact natural sciences could not, and still cannot, avoid basing their thought systems on certain hypotheses. In classical physics, up to the end of the 18th century, one of the working hypotheses, arrived at either unconsciously or half-consciously, was that space had three dimensions, an idea which was never questioned. The fact was always accepted, and perspective drawings of physical events, diagrams, or experiments, were always in accordance with that theory. Only when this theory is abandoned does one wonder how such a thing could ever have been believed. How did one come by such an idea? Why were we so caught that nobody ever doubted or even discussed the matter? It was accepted as a self-evident fact, but what was at the root of it? Johannes Kepler, one of the fathers of modern or classic physics, said that naturally space must have three dimensions because of the Trinity! So our readiness to believe that space has three dimensions is a more recent offspring of the Christian trinitarian idea.”
— Marie-Louise von Franz, Alchemy: An Introduction to the Symbolism and the Psychology
Gravitational Waves in the Space-Time Continuum
Einstein's Theories of Relativity
Einstein has two theories of relativity. The first is The Theory of Special Relativity (1905). This is a theory of mechanics that correctly describes the motions of objects moving near the speed of light. This theory predicts that mass increases with velocity. The equation is E=MC^2 or Energy = Mass × Speed of Light ^2.
In 1916, Einstein proposed the Theory of General Relativity, which generalized his Theory of Special Relativity and had the first predictions of gravitational waves. It implied a few things.
Space-Time is a 4-Dimensional continuum.
Principle of equivalence of gravitational and inertial mass.
This suggests that Mass-Energy distorts the fabric of space-time in a predictable way (gravitational waves). It also implies
Strong gravitational force makes time slow down.
Light is altered by gravity
Gravity in strong gravitational fields will no longer obey Newton's Inverse-Square Law.
What is Newton's Inverse-Square Law?
Newton's Inverse-Square Law suggests that the force of gravity between any two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the separation distance between the two centers.
Stephen Hawking's Theory of Everything
Stephen Hawking's Theory of Everything is the solution to Einstein's equation in his Theory of General Relativity. It says that the mass density of the universe exceeds the critical density.
Critical Density: amount of mass needed to make a universe adopt a flat geometry.
This theory states that when the universe gets too big it will crash back into its center in a "Big Crunch" creating giant black hole. The energy from this "Big Crunch" will rebound and create a new "Big Bang".
Big Crunch: hypothetical scenario for the end of the known universe. The expansion of the universe will reverse and collapse on itself. The energy generated will create a new Big Bang, creating a new universe.
Big Bang: Matter will expand from a single point from a state of high density and matter. This will mark the birth of a new universe.
Basic Facts about Gravitational Waves
Invisible "ripples" in the Space-Time Continuum
Travel at the speed of light
186,000 miles per second / 299,337.984 Kilometers per second
11,160,000 miles per minute / 17,960,279.04 Kilometers per minute
669,600,000 miles per hour / 1,077,616,742.4 Kilometers per hour
There are four (4) defined categories
Continuous
Stochastic
Burst
Compact Binary Inspiral
What is LIGO?
The first proof of the existence of gravitational waves came in 1974. 20+ years after Einstein's death.
The first physical proof came in 2015, 100 years after his theory was published. The waves were detected by LIGO.
LIGO- Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory
The waves detected in 2015 came from 2 black holes that collided 1.3 billion years ago in the constellation Hydra. 1.3 billion years ago multicellular life was just beginning to spread on Earth, it was before the time of the dinosaurs!
Continuous Gravitational Waves
Produced by a single spinning massive object.
Caused by imperfections on the surface.
The spin rate of the object is constant. The waves are come at a continuous frequency.
Stochastic Gravitational Waves
Smalles waves
Hardest to detect
Possibly caused by remnants of gravitational radiation left over from the Big Bang
Could possibly allow us to look at the history of the Universe.
Small waves from every direction mixed together.
Burst Gravitational Waves
Never been detected.
Like ever.
Never ever.
Not once.
Nope
No
N E V E R
We don't know anything about them.
If we learn about them they could reveal the greatest revolutionary information about the universe.
Compact Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves
All waves detected by LIGO fall into this category.
Produced by orbiting pairs of massive and dense objects. (Neutron Stars, Black Holes)
Three (3) subclasses
Binary Neutron Star (BNS) // Two (2) Neutron Stars colliding
Binary Black Hole (BBH) // Two (2) Black Holes colliding
Neutron Star- Black Hole Binary (NSBH) // A black hole and a neutron star colliding
Each subclass creates its own unique wave pattern.
Waves are all caused by the smae mechanism called an "inspiral".
Occur over millions of years.
Over eons the objects orbit closer together.
The closer they get, the faster they spin.
Sources Used:
On The Shoulders Of Giants by Stephen Hawking
Oxford Astronomy Encyclopedia



@watch-out-idiot-passing-through @nasa


In Roman mythology, the god Jupiter drew a veil of clouds around himself to hide his mischief. It was only Jupiter’s wife, the goddess Juno, who could peer through the clouds and reveal Jupiter’s true nature. Our @NASAJuno spacecraft is looking beneath the clouds of the massive gas giant, not seeking signs of misbehavior, but helping us to understand the planet’s structure and history… Now, @NASAJuno just published its first findings on the amount of water in the gas giant’s atmosphere. The Juno results estimate that at the equator, water makes up about 0.25% of the molecules in Jupiter’s atmosphere — almost three times that of the Sun. An accurate total estimate of this water is critical to solving the mystery of how our solar system formed.
The JunoCam imager aboard Juno captured this image of Jupiter’s southern equatorial region on Sept. 1, 2017. The bottom image is oriented so Jupiter’s poles (not visible) run left-to-right of frame.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Kevin M. Gill
Celebrating Spitzer, One of NASA’s Great Observatories
As the Spitzer Space Telescope’s 16-year mission ends, we’re celebrating the legacy of our infrared explorer. It was one of four Great Observatories – powerful telescopes also including Hubble, Chandra and Compton – designed to observe the cosmos in different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Light our eyes can see
The part of the spectrum we can see is called, predictably, visible light. But that’s just a small segment of all the wavelengths of the spectrum. The Hubble Space Telescope observes primarily in the visible spectrum. Our Chandra X-ray Observatory is designed to detect (you guessed it) X-ray emissions from very hot regions of the universe, like exploded stars and matter around black holes. Our Compton Gamma Ray Observatory, retired in 2000, produced the first all-sky survey in gamma rays, the most energetic and penetrating form of light.

Then there’s infrared…
Infrared radiation, or infrared light, is another type of energy that we can’t see but can feel as heat. All objects in the universe emit some level of infrared radiation, whether they’re hot or cold. Spitzer used its infrared instrument to make discoveries in our solar system (including Saturn’s largest ring) all the way to the edge of the universe. From stars being born to planets beyond our solar system (like the seven Earth-size exoplanets around the star TRAPPIST-1), Spitzer’s science discoveries will continue to inspire the world for years to come.

Multiple wavelengths
Together, the work of the Great Observatories gave us a more complete view and understanding of our universe.

Hubble and Chandra will continue exploring our universe, and next year they’ll be joined by an even more powerful observatory … the James Webb Space Telescope!

Many of Spitzer’s breakthroughs will be studied more precisely with the Webb Space Telescope. Like Spitzer, Webb is specialized for infrared light. But with its giant gold-coated beryllium mirror and nine new technologies, Webb is about 1,000 times more powerful. The forthcoming telescope will be able to push Spitzer’s science findings to new frontiers, from identifying chemicals in exoplanet atmospheres to locating some of the first galaxies to form after the Big Bang.
We can’t wait for another explorer to join our space telescope superteam!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Taking Solar Science to New Heights
We’re on the verge of launching a new spacecraft to the Sun to take the first-ever images of the Sun’s north and south poles!

Credit: ESA/ATG medialab
Solar Orbiter is a collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA. After it launches — as soon as Feb. 9 — it will use Earth’s and Venus’s gravity to swing itself out of the ecliptic plane — the swath of space, roughly aligned with the Sun’s equator, where all the planets orbit. From there, Solar Orbiter’s bird’s eye view will give it the first-ever look at the Sun’s poles.

Credit: ESA/ATG medialab
The Sun plays a central role in shaping space around us. Its massive magnetic field stretches far beyond Pluto, paving a superhighway for charged solar particles known as the solar wind. When bursts of solar wind hit Earth, they can spark space weather storms that interfere with our GPS and communications satellites — at their worst, they can even threaten astronauts.
To prepare for potential solar storms, scientists monitor the Sun’s magnetic field. But from our perspective near Earth and from other satellites roughly aligned with Earth’s orbit, we can only see a sidelong view of the Sun’s poles. It’s a bit like trying to study Mount Everest’s summit from the base of the mountain.

Solar Orbiter will study the Sun’s magnetic field at the poles using a combination of in situ instruments — which study the environment right around the spacecraft — and cameras that look at the Sun, its atmosphere and outflowing material in different types of light. Scientists hope this new view will help us understand not only the Sun’s day-to-day activity, but also its roughly 11-year activity cycles, thought to be tied to large-scales changes in the Sun’s magnetic field.
Solar Orbiter will fly within the orbit of Mercury — closer to our star than any Sun-facing cameras have ever gone — so the spacecraft relies on cutting-edge technology to beat the heat.

Credit: ESA/ATG medialab
Solar Orbiter has a custom-designed titanium heat shield with a calcium phosphate coating that withstands temperatures more than 900 degrees Fahrenheit — 13 times the solar heating that spacecraft face in Earth orbit. Five of the cameras look at the Sun through peepholes in that heat shield; one observes the solar wind out the side.
Over the mission’s seven-year lifetime, Solar Orbiter will reach an inclination of 24 degrees above the Sun’s equator, increasing to 33 degrees with an additional three years of extended mission operations. At closest approach the spacecraft will pass within 26 million miles of the Sun.
Solar Orbiter will be our second major mission to the inner solar system in recent years, following on August 2018’s launch of Parker Solar Probe. Parker has completed four close solar passes and will fly within 4 million miles of the Sun at closest approach.

Solar Orbiter (green) and Parker Solar Probe (blue) will study the Sun in tandem.
The two spacecraft will work together: As Parker samples solar particles up close, Solar Orbiter will capture imagery from farther away, contextualizing the observations. The two spacecraft will also occasionally align to measure the same magnetic field lines or streams of solar wind at different times.
Watch the launch

The booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is lifted into the vertical position at the Vertical Integration Facility near Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Jan. 6, 2020. Credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
Solar Orbiter is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, during a two-hour window that opens at 11:03 p.m. EST. The spacecraft will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 411 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
Launch coverage begins at 10:30 p.m. EST on Feb. 9 at nasa.gov/live. Stay up to date with mission at nasa.gov/solarorbiter!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com