How Does Sand From Sahara End Up In Your Windshield ?
How does sand from Sahara end up in your windshield ?

TBH cleaning your car is a rather mundane task. But when you fill your head with some interesting physics the task actually gets rather pretty interesting. Here’s some good for thought on such an occasion :
The dust on your windshield might actually be from the Sahara desert
To understand how, lets start with some simple physics.
The stacked ball drop
You basically take couple of balls, align them up and drop them to the ground. The ball at the top reaches the most highest due to the subsequent transfer of energy from the other balls.

Source Video : Physics Girl
Here is an exaggerated but amazing slow motion of the same energy transfer with a water balloon. Notice how the transfer of energy takes place between the water balloon and the tennis ball.

Source Video : Slow Mo Lab
Sandstorms in the desert

Sandstorms/ Dust storms as you might be aware, are pretty common in the desert. . Dust storms arise when a gust front or other strong wind blows loose sand and dirt from a dry surface.

And this can cause something phenomenal to happen:
If the wind speed is sufficient then larger sand particles can propel finer ones high into the atmosphere. ( just like the stacked ball )
Then these fine particles are caught in the global wind pattern and are transported across the globe until they fall down to the earth as rain.
How cool is that ! Have a great day!
* Tracking saharan dust in 3D - NASA video
** All the World’s a Stage … for Dust - NASA article
** Wiki on Saltation
More Posts from T-sci-eng and Others

You might be an engineer if you know how long a zeptosecond is. (It's a trillionth of a billionth of a second!) http://ow.ly/uUUb30caXrH
coolest physics thing that u know??
The coolest physics thing that I know keeps changing over time. But here is one that is extremely fascinating ( and also exaggerated for the effect ; but true! ):
Person living at the top of a skyscraper experiences time faster than one at the bottom
It is a known fact that the higher you are in the earth’s ** atmosphere, the lesser the effect of gravity is.
But the lesser the effect of gravity is, the faster the time ticks.

By how much you ask? Even if you live on the top floor of the Burj Khalifa your entire life, you would have aged more only by a few milliseconds than your friends at the bottom.
( Sure, doesn’t seem like much, but hell would break loose if we don’t consider this on the bigger scale of things )
This is known as Gravitational time dilation and is at the foundations of General Theory of Relativity. (More about this in an upcoming post)
Have a great day and thanks for asking!
EDIT: ** Lets just say hypothetically the earth is not spinning( just to ignore special relativistic effects) and we are looking at only the effects of height.





Impressive artwork.
Dr. Greg Dunn (artist and neuroscientist) and Dr. Brian Edwards (artist and applied physicist) created Self Reflected to elucidate the nature of human consciousness, bridging the connection between the mysterious three pound macroscopic brain and the microscopic behavior of neurons. Self Reflected offers an unprecedented insight of the brain into itself, revealing through a technique called reflective microetching the enormous scope of beautiful and delicately balanced neural choreographies designed to reflect what is occurring in our own minds as we observe this work of art. Self Reflected was created to remind us that the most marvelous machine in the known universe is at the core of our being and is the root of our shared humanity.
h-t New Scientist: Brain images display the beauty and complexity of consciousness
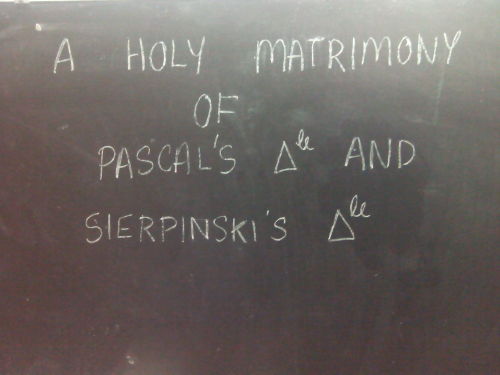
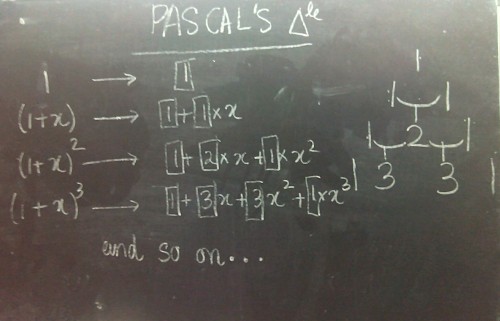

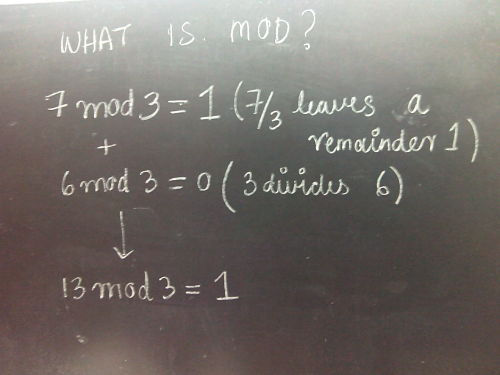




Nature manifests itself in patterns. The interweaving of math with these patterns produces euphoria
What do you see ? Let use know in the comments :)
Quench your thirst for knowledge with:
More about Pascals triangle and Binary Trees - Vihart
Scary Sierpinski Skull Time
Mathematical secrets of the pascal’s triangle
Code to generate Pascal’s triangle mod in Python

The ocean is where the aliens live.
Transcript under the cut.
Patreon | Instagram | Facebook | Twitter | deviantArt
Keep reading

Chances of hypersonic travel heat up with new materials discovery
Researchers at The University of Manchester in collaboration with Central South University (CSU), China, have created a new kind of ceramic coating that could revolutionise hypersonic travel for air, space and defense purposes.
Hypersonic travel means moving at Mach five or above, which is at least five times faster than the speed of sound. When moving at such velocity the heat generated by air and gas in the atmosphere is extremely hot and can have a serious impact on an aircraft or projectile’s structural integrity. That is because he temperatures hitting the aircraft can reach anywhere from 2,000 to 3,000 °C.
The structural problems are primarily caused by processes called oxidation and ablation. This is the when extremely hot air and gas remove surface layers from the metallic materials of the aircraft or object travelling at such high speeds. To combat the problem materials called ultra-high temperature ceramics (UHTCs) are needed in aero-engines and hypersonic vehicles such as rockets, re-entry spacecraft and defence projectiles.
But, at present, even conventional UHTCs can’t currently satisfy the associated ablation requirements of travelling at such extreme speeds and temperatures. However, the researchers at The University of Manchester’s and the Royce Institute, in collaboration with the Central South University of China, have designed and fabricated a new carbide coating that is vastly superior in resisting temperatures up to 3,000 °C, when compared to existing UHTCs.





Composites: Papercrete
Composites are materials composed of other materials in combination, often with a matrix that binds together fibers of some kind. Papercrete gets its name from its components, paper and concrete, though it is technically composed of cement, not concrete. In papercrete, a composite of paper and cement, the cement makes up the binding matrix that holds the paper fibers together.
Paper is composed of a natural polymer, cellulose, the structure of which can be seen in the bottom image above and fibers of which can be seen in the top left and middle right images. The fibers get coated with cement, often Portland cement, and lend strength to the new material that could not be found in the cement alone. (Paper is not only made of cellulose, but it is a key component which makes papercrete possible. Aside from paper and cement, papercrete is also made with water and some form of sand or earth - other materials can be used as well, just like in concrete).
The material resulting from this mixture, papercrete, has excellent sound absorption, is flame and fungus retardant as well as bug and rodent repellent, and is relatively light. More flexible then rock or regular concrete, papercrete is useful in earthquake prone areas. Though not the best load-bearing material, papercrete is a great insulator. Like any composite however, the exact formula used to produce the material can alter the properties significantly. Adding sand or glass strengthens papercrete and makes it more flame retardant, but also increases its weight.
One of the beneficial things about papercrete is that almost any paper can be used to create it - cardboard, magazine paper, junk mail, newspaper, and other forms. Some work better than others but almost all can be used. Using waste papers such as these prevents them from entering landfills and allows paper to be recycled in a different way.
Downsides of papercrete include its lower strength and durability, as well as the fact that - as of now - there is no code or standardization to its manufacture or use, limiting the projects it can be used in. A fair amount of papercrete is made by individuals working on ‘do it yourself’ projects.
Sources: ( 1 - images 1, 2, 4, and 5 ) ( 2 ) ( 3 )
Image sources: (Middle left)





Why most metals are silver (but copper and gold aren’t)
If we want to understand what gives a metal its color we first need to understand a little bit about the definition of a metal. Metals are materials that experience metallic bonding - wherein the atoms are so close that there is a veritable “sea of electrons” in the substance. (This is also what makes metals conductors, but that’s another story). Basically each atom donates an electron or two that is free to flow throughout the material, unattached to any particular nucleus.
This proximity leads to an overlap in the allowed energy levels of electrons (shown in the lower left hand image above); basically the higher empty electronic levels are so close to the uppermost filled levels (also called the Fermi level) that they form an essentially continuous band of allowed energies.
Now, backtracking a little bit, color in a substance is caused when a material doesn’t absorb a particular wavelength of light. Because of the empty energy levels mentioned above, metals generally can absorb all wavelengths of light in the visible spectrum. This implies that a metal should look black, except that the excited electron can immediately fall back to the state that it came from, emitting exactly the same energy, causing a flat piece of metal to appear reflective. Thus, the reason why most metals are silver. (Also, the flatter a metal, the more reflective, thanks to diffuse vs. specular reflection).
For a few select metals, like copper and gold, the absorption and emission of photons are noticeably dependent on wavelength across the visible part of the spectrum. The graph in the lower right image above shows the reflectance of aluminum, silver, and gold, including wavelengths in the infrared and ultraviolet. Aluminum is pretty reflective overall, and silver is highly reflective in the visible region (about 400 to 700 nm), but gold clearly absorbs wavelengths about 500 nm or below. Thus, it most strongly reflects yellow, giving it its characteristic appearance.
Sources: (first image), 2 (second image), 3 (third image), 4
-
 leejs1234567 liked this · 5 years ago
leejs1234567 liked this · 5 years ago -
 mylastshadow liked this · 7 years ago
mylastshadow liked this · 7 years ago -
 roseofsomekind reblogged this · 7 years ago
roseofsomekind reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 roseofsomekind liked this · 7 years ago
roseofsomekind liked this · 7 years ago -
 mdougforks reblogged this · 7 years ago
mdougforks reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 suszottzitark-blog liked this · 7 years ago
suszottzitark-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 limoneno-r liked this · 7 years ago
limoneno-r liked this · 7 years ago -
 tuba-engine liked this · 7 years ago
tuba-engine liked this · 7 years ago -
 sultan4h liked this · 7 years ago
sultan4h liked this · 7 years ago -
 werdulniwas-blog liked this · 7 years ago
werdulniwas-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 stumm13 liked this · 7 years ago
stumm13 liked this · 7 years ago -
 mystical-vulcan liked this · 7 years ago
mystical-vulcan liked this · 7 years ago -
 artbeet liked this · 7 years ago
artbeet liked this · 7 years ago -
 garydeanf-blog liked this · 7 years ago
garydeanf-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 shakespeareswag liked this · 7 years ago
shakespeareswag liked this · 7 years ago -
 a-fucking-spook-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
a-fucking-spook-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 a-fucking-spook-blog liked this · 7 years ago
a-fucking-spook-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 snowsoar liked this · 7 years ago
snowsoar liked this · 7 years ago -
 themorethemelanin liked this · 7 years ago
themorethemelanin liked this · 7 years ago -
 xawopa liked this · 7 years ago
xawopa liked this · 7 years ago -
 dalekhallows liked this · 7 years ago
dalekhallows liked this · 7 years ago -
 moneymakerbootyshaker liked this · 7 years ago
moneymakerbootyshaker liked this · 7 years ago -
 chirpchirrup liked this · 7 years ago
chirpchirrup liked this · 7 years ago -
 tonyslayer reblogged this · 7 years ago
tonyslayer reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 tonyslayer liked this · 7 years ago
tonyslayer liked this · 7 years ago -
 moonsofmoons liked this · 7 years ago
moonsofmoons liked this · 7 years ago -
 semics-blog liked this · 7 years ago
semics-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 iamhisgloriouspurpose liked this · 7 years ago
iamhisgloriouspurpose liked this · 7 years ago -
 thidfass liked this · 7 years ago
thidfass liked this · 7 years ago -
 jlgnorcross liked this · 7 years ago
jlgnorcross liked this · 7 years ago -
 thedreamerdelta liked this · 7 years ago
thedreamerdelta liked this · 7 years ago -
 damageditem liked this · 7 years ago
damageditem liked this · 7 years ago -
 the-game-is-lokid reblogged this · 7 years ago
the-game-is-lokid reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 the-game-is-lokid liked this · 7 years ago
the-game-is-lokid liked this · 7 years ago -
 burningarbiterheart reblogged this · 7 years ago
burningarbiterheart reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 writernotwaiting reblogged this · 7 years ago
writernotwaiting reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 president-of-the-united-states liked this · 7 years ago
president-of-the-united-states liked this · 7 years ago -
 enderiox reblogged this · 7 years ago
enderiox reblogged this · 7 years ago









