What Inspired You To Attempt A SPOCS Project?
What inspired you to attempt a SPOCS project?
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Photographing Planets with the Roman Space Telescope
Nearly 100 years ago, astronomer Bernard Lyot invented the coronagraph – a device that made it possible to recreate a total solar eclipse by blocking the Sun’s light. That helped scientists study the Sun’s corona, which is the outermost part of our star’s atmosphere that’s usually hidden by bright light from its surface.

Our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, now under construction, will test out a much more advanced version of the same thing. Roman’s Coronagraph Instrument will use special masks to block the glare from host stars but allow the light from dimmer, orbiting planets to filter through. It will also have self-flexing mirrors that will measure and subtract starlight automatically.

This glare-blocking prowess is important because planets can be billions of times dimmer than their host stars! Roman’s high-tech shades will help us take pictures of planets we wouldn’t be able to photograph using any other current telescopes.

Other observatories mainly use this planet-hunting method, called direct imaging, from the ground to photograph huge, bright planets called “super-Jupiters” in infrared light. These worlds can be dozens of times more massive than Jupiter, and they’re so young that they glow brightly thanks to heat left over from their formation. That glow makes them detectable in infrared light.

Roman will take advanced planet-imaging tech to space to get even higher-quality pictures. And while it’s known for being an infrared telescope, Roman will actually photograph planets in visible light, like our eyes can see. That means it will be able to see smaller, older, colder worlds orbiting close to their host stars. Roman could even snap the first-ever image of a planet like Jupiter orbiting a star like our Sun.
Astronomers would ultimately like to take pictures of planets like Earth as part of the search for potentially habitable worlds. Roman’s direct imaging efforts will move us a giant leap in that direction!

And direct imaging is just one component of Roman’s planet-hunting plans. The mission will also use a light-bending method called microlensing to find other worlds, including rogue planets that wander the galaxy untethered to any stars. Scientists also expect Roman to discover 100,000 planets as they cross in front of their host stars!

Find out more about the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope on Twitter and Facebook, and about the person from which the mission draws its name.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Summer Starts in the Northern Hemisphere!
Today is the first day of summer in the Northern Hemisphere -- the solstice! People located in the Northern Hemisphere will have the longest day of the year today, and people located in the Southern Hemisphere will have the shortest day of the year.

The angle between the Earth’s orbit and the axis of its rotation creates our seasons, tilting each hemisphere toward the Sun during summer in that half of the Earth. This is summer in the Northern Hemisphere, and winter in the Southern Hemisphere. The other half of the year, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun, creating winter in the north and summer in the south.

Solstices happen twice per year, at the points in Earth’s orbit where this tilt is most pronounced.

These days are the longest (in the summer hemisphere) and shortest (in the winter hemisphere) of the year, and mark the change of seasons to summer and winter, respectively.
For more Earth science, follow NASA Earth on Twitter, on Facebook, or on the web.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Does space have a standard time or do you rely on the time zones on Earth while you are in space?
Great question. Really it is up to the particular space agency/mission which time zone they use. For example, since the International Space Station is a collaboration between NASA, the Russian Space Agency, the European Space Agency, the Japanese Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency, we came up with the compromise of operating on Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). So, Space Station time is the same as London time! The International Space Station orbits our planet every 90 minutes, so of course we’re transiting across multiple time zones constantly.
Going for GOLD
On Jan. 25, we’re going for GOLD!
We’re launching an instrument called Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk, GOLD for short. It’s a new mission that will study a complicated — and not yet fully understood — region of near-Earth space, called the ionosphere.

Space is not completely empty: It’s teeming with fast-moving energized particles and electric and magnetic fields that guide their motion. At the boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and space, these particles and fields — the ionosphere — co-exist with the upper reaches of the neutral atmosphere.

That makes this a complicated place. Big events in the lower atmosphere, like hurricanes or tsunamis, can create waves that travel all the way up to that interface to space, changing the wind patterns and causing disruptions.

It’s also affected by space weather. The Sun is a dynamic star, and it releases spurts of energized particles and blasts of solar material carrying electric and magnetic fields that travel out through the solar system. Depending on their direction, these bursts have the potential to disrupt space near Earth.

This combination of factors makes it hard to predict changes in the ionosphere — and that can have a big impact. Communications signals, like radio waves and signals that make our GPS systems work, travel through this region, and sudden changes can distort them or even cut them off completely.

Low-Earth orbiting satellites — including the International Space Station — also fly through the ionosphere, so understanding how it fluctuates is important for protecting these satellites and astronauts.

GOLD is a spectrograph, an instrument that breaks light down into its component wavelengths, measuring their intensities. Breaking light up like this helps scientists see the behavior of individual chemical elements — for instance, separating the amount of oxygen versus nitrogen. GOLD sees in far ultraviolet light, a type of light that’s invisible to our eyes.

GOLD is a hosted payload. The instrument is hitching a ride aboard SES-14, a commercial communications satellite built by Airbus for SES Government Solutions, which owns and operates the satellite.
Also launching this year is the Ionospheric Connection Explorer, or ICON, which will also study the ionosphere and neutral upper atmosphere. But while GOLD will fly in geostationary orbit some 22,000 miles above the Western Hemisphere, ICON will fly just 350 miles above Earth, able to gather close up images of this region.

Together, these missions give us an unprecedented look at the ionosphere and upper atmosphere, helping us understand the very nature of how our planet interacts with space.
To learn more about this region of space and the GOLD mission, visit: nasa.gov/gold.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
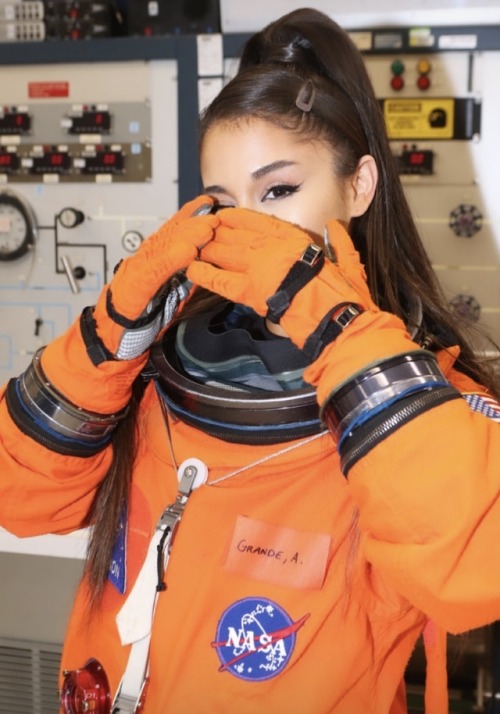




Ariana Grande got some space at N-A-S-A. Get yours too.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Did you have an innate talent for math? Or did you struggle and practiced until you understood it? I wanted to become an aerospace engineer but after taking a class I decided psychology was more suited for me because I struggled with equations but thrived with the psychological terms
Anything you don’t know is hard until you learn it. There are a few geniuses in the world, but most people study and work hard to learn what they love. Even the smartest amongst you actually put in a lot of time to learn the things that they want, and no one is an exception. You have to put in the time.
What Does Two Decades of Rain and Snow Show Us?
You are seeing the culmination of almost twenty years of rain and snow, all at once.

For the first time, we have combined and remastered the satellite measurements from two of our precipitation spacecraft to create our most detailed picture of our planet’s rain and snowfall. This new record will help scientists better understand normal and extreme rain and snowfall around the world and how these weather events may change in a warming climate.

The Most Extreme Places on Earth
Using this new two-decade record, we can see the most extreme places on Earth.
The wettest places on our planet occur over oceans. These extremely wet locations tend to be very concentrated and over small regions.
A region off the coast of Indonesia receives on average 279 inches of rain per year.

An area off the coast of Colombia sees on average 360 inches of rain per year.

The driest places on Earth are more widespread. Two of the driest places on Earth are also next to cold ocean waters. In these parts of the ocean, it rains as little as it does in the desert -- they’re also known as ocean deserts!
Just two thousand miles to the south of Colombia is one of the driest areas, the Atacama Desert in Chile that receives on average 0.64 inches of rain per year.

Across the Atlantic Ocean, Namibia experiences on average 0.49 inches of rain a year and Egypt gets on average 0.04 inches of rain per year.

Global Patterns
As we move from January to December, we can see the seasons shift across the world.

During the summer in the Northern Hemisphere, massive monsoons move over India and Southeast Asia.

We can also see dynamic swirling patterns in the Southern Ocean, which scientists consider one of our planet’s last great unknowns.

Close-up Patterns
This new record also reveals typical patterns of rain and snow at different times of the day -- a pattern known as the diurnal cycle.
As the Sun heats up Earth’s surface during the day, rainfall occurs over land. In Florida, sea breezes from the Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic Ocean feed the storms causing them to peak in the afternoon. At night, storms move over the ocean.

In the winter months in the U.S. west coast, the coastal regions generally receive similar amounts of rain and snow throughout the day. Here, precipitation is driven less from the daily heating of the Sun and more from the Pacific Ocean bringing in atmospheric rivers -- corridors of intense water vapor in the atmosphere.

This new record marks a major milestone in the effort to generate a long-term record of rain and snow. Not only does this long record improve our understanding of rain and snow as our planet changes, but it is a vital tool for other agencies and researchers to understand and predict floods, landslides, disease outbreaks and agricultural production.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
🚀 A New Era of Human Spaceflight
Our Commercial Crew Program has worked with several American aerospace industry companies to facilitate the development of U.S. human spaceflight systems since 2010. The goal is to have safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from the International Space Station and foster commercial access to other potential low-Earth orbit destinations.

We selected Boeing and SpaceX in September 2014 to transport crew to the International Space Station from the United States. These integrated spacecraft, rockets and associated systems will carry up to four astronauts on NASA missions, maintaining a space station crew of seven to maximize time dedicated to scientific research on the orbiting laboratory

We begin a new era of human spaceflight as American astronauts will once again launch on an American spacecraft and rocket from American soil to the International Space Station.

As part of our Commercial Crew Program, NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley will fly on SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft for an extended stay at the space station for the Demo-2 mission. Launch is scheduled for 4:33 p.m. EDT on Wednesday, May 27.

Demo-2 will be SpaceX’s final test flight to validate its crew transportation system, including the Crew Dragon spacecraft, Falcon 9 rocket, launch pad and operations capabilities. While docked to the space station, the crew will run tests to ensure the Crew Dragon is capable of remaining connected to the station for up to 210 days on future missions.

Our Commercial Crew Program is working with the American aerospace industry as companies develop and operate a new generation of spacecraft and launch systems capable of carrying crews to low-Earth orbit and the International Space Station. Commercial transportation to and from the station will provide expanded utility, additional research time and broader opportunities for discovery on the orbiting laboratory.

The station is a critical testbed for us to understand and overcome the challenges of long-duration spaceflight. As commercial companies focus on providing human transportation services to and from low-Earth orbit, we are freed up to focus on building spacecraft and rockets for deep space missions.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

NASA Spotlight: Brandon Rodriguez, Jet Propulsion Laboratory Education Specialist
Brandon Rodriguez is an education specialist at our Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California where he provides resources and training to K-12 schools across the Southwest. Working with a team at JPL, he develops content for classroom teachers, visits schools and speaks with students and trains future teachers to bring NASA into their classroom. When he’s not in the classroom, Brandon’s job takes him on research expeditions all around the world, studying our planet’s extreme environments.
Fun fact: Brandon wakes up every morning to teach an 8 a.m. physics class at a charter school before heading to JPL and clocking in at his full time job. When asked why? He shared, “The truth is that I really feel so much better about my role knowing that we’re not ‘telling’ teachers what to do from our ivory tower. Instead, I can “share” with teachers what I know works not just in theory, but because I’m still there in the classroom doing it myself.” - Brandon Rodriguez
Brandon took time from exciting the next generation of explorers to answer some questions about his life and his career:
What inspired you to work in the educational department at NASA?
I was over the moon when I got a call from NASA Education. I began my career as a research scientist, doing alternative energy work as a chemist. After seven years in the field, I began to feel as if I had a moral responsibility to bring access to science to a the next generation. To do so, I quit my job in science and became a high school science teacher. When NASA called, they asked me if I wanted a way to be both a scientist and an educator- how could I resist?

You were born in Venezuela and came to the U.S. when you were 12 years old. Can you tell us the story of why and how you came to America?
I haven't been back to Venezuela since I was very young, which has been very difficult for me. Being an immigrant in the USA sometimes feels like you're an outsider of both sides: I'm not truly Latin, nor am I an American. When I was young, I struggled with this in ways I couldn't articulate, which manifested in a lot of anger and got me in quite a bit of trouble. Coming to California and working in schools that are not only primarily Latinx students, but also first generation Latinx has really helped me process that feeling, because it's something I can share with those kids. What was once an alienating force has become a very effective tool for my teaching practice.
Does your job take you on any adventures outside of the classroom and if so, what have been your favorite endeavors?
I'm so fortunate that my role takes me all over the world and into environments that allow to me to continue to develop while still sharing my strengths with the education community. I visit schools all over California and the Southwest of the USA to bring professional development to teachers passionate about science. But this year, I was also able to join the Ocean Exploration Trust aboard the EV Nautilus as we explored the Pacific Remote Island National Marine Monument. We were at sea for 23 days, sailing from American Samoa to Hawaii, using submersible remotely operated vehicles to explore the ocean floor.

Image Credit: Nautilus Live
We collected coral and rock samples from places no one has ever explored before, and observed some amazing species of marine creatures along the way.

Image Credit: Nautilus Live
What keeps you motivated to go to work every day?
There's no greater motivation than seeing the product of your hard work, and I get that everyday through students. I get to bring them NASA research that is "hot off the press" in ways that their textbooks never can. They see pictures not online or on worksheets, but from earlier that day as I walked through JPL. It is clearly that much more real and tangible to them when they can access it through their teacher and their community.

Do you have any tips for people struggling with their science and math classes?
As someone who struggled- especially in college- I want people to know that what they struggle with isn't science, it's science classes. The world of research doesn't have exams; it doesn't have blanks to be filled in or facts to be memorized. Science is exploring the unknown. Yes, of course we need the tools to properly explore, and that usually means building a strong academic foundation. But it helped me to differentiate the end goal from the process: I was bad at science tests, but I wanted to someday be very good at science. I could persevere through the former if it got me to the latter.
If you could safely visit any planet, star, or solar system, where would you visit and what would you want to learn?
Europa, without a doubt. Imagine if we found even simple life once more in our solar system- and outside of the habitable zone, no less. What would this mean for finding life outside of our solar system as a result? We would surely need to conclude that our sky is filled with alien worlds looking back at us.

Is there a moment or project that you feel defined (or significantly impacted) your career up to today?
While I never worked closely with the mission, Insight was a really important project for me. It's the first time while at JPL I was able to see the construction, launch and landing of a mission.
If you could name a spaceship, what would you name it?
For as long as I can remember, I've been watching and reading science fiction, and I continue to be amazed at how fiction informs reality. How long ago was it that in Star Trek, the crew would be handing around these futuristic computer tablets that decades later would become common iPads? In their honor, I would be delighted if we named a ship Enterprise.
Thanks so much Brandon!
Additional Image Credit: MLParker Media
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
In addition to the Mercury transit of the sun today, there are a few other things you should know about our solar system this week:
1. Mars, Ready for its Close-Up

Mars will soon be closer to Earth than it has been for 11 years, presenting a great opportunity for backyard sky watchers.
2. Fire and Ice
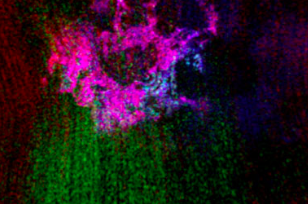
Our spacecraft have an even closer view of Mars, and that fact regularly leads to some intriguing discoveries. The latest: volcanoes may have erupted beneath an ice sheet there billions of years ago. The above image is a mineral map of part of the Martian surface.
3. Icy Hydra

Meanwhile, our New Horizons spacecraft has sent home the first compositional data about Pluto's four small moons. The new data show the surface of Hydra is dominated by nearly pristine water ice--confirming hints that scientists picked up in images showing Hydra's highly reflective surface.
4. Ceres, Ever Sharper

The mission director for our Dawn mission writes, "Ceres, which only last year was hardly more than a fuzzy blob against the stars, is now a richly detailed world, and our portrait grows more elaborate every day."
5. Join us at Jupiter

Our Juno mission arrives at the giant planet on Jul. 4. Meanwhile, all amateur astronomers are invited to take part in a worldwide effort to identify potential observations for the spacecraft to make once it's in orbit. Find out how to join HERE.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 lazilyyoungneek liked this · 3 years ago
lazilyyoungneek liked this · 3 years ago -
 shelly-bee-world liked this · 3 years ago
shelly-bee-world liked this · 3 years ago -
 syedzada-abuzar22 liked this · 3 years ago
syedzada-abuzar22 liked this · 3 years ago -
 belindasvasconcelos liked this · 3 years ago
belindasvasconcelos liked this · 3 years ago -
 littlemissrand liked this · 3 years ago
littlemissrand liked this · 3 years ago -
 freeminderone liked this · 3 years ago
freeminderone liked this · 3 years ago -
 silentninjacat2 liked this · 3 years ago
silentninjacat2 liked this · 3 years ago -
 dragons-barb liked this · 3 years ago
dragons-barb liked this · 3 years ago -
 ringo6143 liked this · 3 years ago
ringo6143 liked this · 3 years ago -
 ehsunassadi liked this · 3 years ago
ehsunassadi liked this · 3 years ago -
 random-acts-of-stupidity liked this · 3 years ago
random-acts-of-stupidity liked this · 3 years ago -
 go-redgirl liked this · 3 years ago
go-redgirl liked this · 3 years ago -
 jamalmofrih-blog liked this · 3 years ago
jamalmofrih-blog liked this · 3 years ago -
 infiniteviking liked this · 3 years ago
infiniteviking liked this · 3 years ago -
 rosaliachristian liked this · 3 years ago
rosaliachristian liked this · 3 years ago -
 sodaisawitch liked this · 3 years ago
sodaisawitch liked this · 3 years ago -
 mrgneiss liked this · 3 years ago
mrgneiss liked this · 3 years ago -
 grapecola liked this · 3 years ago
grapecola liked this · 3 years ago -
 lemons-and-gremlins-in-your-area liked this · 3 years ago
lemons-and-gremlins-in-your-area liked this · 3 years ago -
 realspaceships liked this · 3 years ago
realspaceships liked this · 3 years ago -
 theknuckleheadninja liked this · 3 years ago
theknuckleheadninja liked this · 3 years ago -
 asch2inspire liked this · 3 years ago
asch2inspire liked this · 3 years ago -
 acnhaddict liked this · 3 years ago
acnhaddict liked this · 3 years ago -
 reflectivewindow liked this · 3 years ago
reflectivewindow liked this · 3 years ago -
 katocrossesthecourtyard liked this · 3 years ago
katocrossesthecourtyard liked this · 3 years ago -
 your-favorite-flower-fairy liked this · 3 years ago
your-favorite-flower-fairy liked this · 3 years ago -
 samucabd liked this · 3 years ago
samucabd liked this · 3 years ago -
 amberrockstar liked this · 3 years ago
amberrockstar liked this · 3 years ago -
 strayadventures liked this · 3 years ago
strayadventures liked this · 3 years ago -
 poti-zz liked this · 3 years ago
poti-zz liked this · 3 years ago -
 pettyofficial liked this · 3 years ago
pettyofficial liked this · 3 years ago -
 fog-on-the-moon liked this · 3 years ago
fog-on-the-moon liked this · 3 years ago -
 2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago
2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago -
 kon-teki liked this · 3 years ago
kon-teki liked this · 3 years ago -
 golddragon387 liked this · 3 years ago
golddragon387 liked this · 3 years ago -
 my1234 liked this · 3 years ago
my1234 liked this · 3 years ago -
 kafkasmelomania liked this · 3 years ago
kafkasmelomania liked this · 3 years ago -
 filantestar liked this · 3 years ago
filantestar liked this · 3 years ago -
 kumatora770 liked this · 3 years ago
kumatora770 liked this · 3 years ago -
 january-summers liked this · 3 years ago
january-summers liked this · 3 years ago -
 weird-is-all-ive-got liked this · 3 years ago
weird-is-all-ive-got liked this · 3 years ago -
 thehkr liked this · 3 years ago
thehkr liked this · 3 years ago -
 16fahri liked this · 3 years ago
16fahri liked this · 3 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts