Dive into your creative stream
Drones - Blog Posts
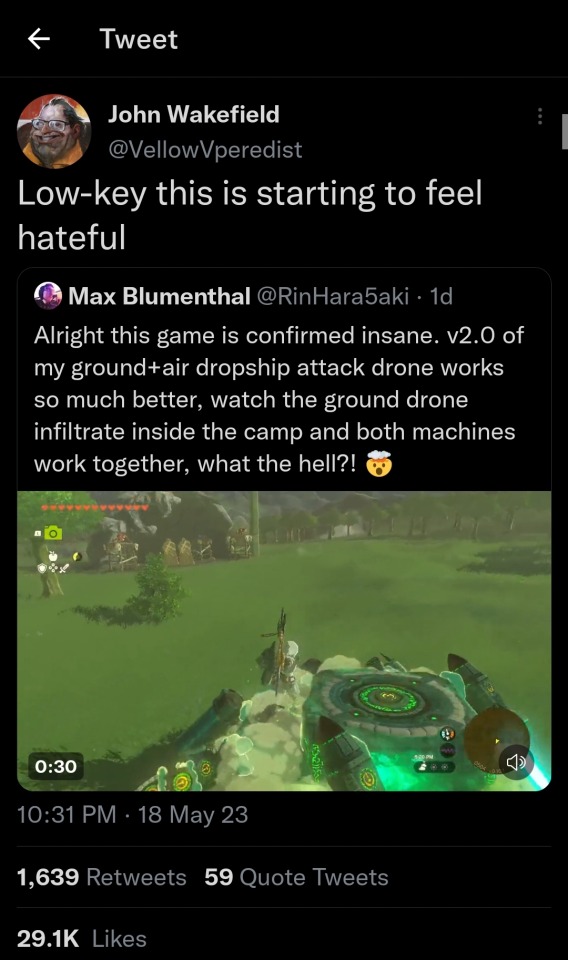
Legend of Zelda: Tears of The Lockheed Martin Kingdom




Here is my new video on my YouTube channel. Drone aerial video of some California cost side.
Like and subscribe
Setting the Standards for Unmanned Aircraft
From advanced wing designs, through the hypersonic frontier, and onward into the era of composite structures, electronic flight controls, and energy efficient flight, our engineers and researchers have led the way in virtually every aeronautic development. And since 2011, aeronautical innovators from around the country have been working on our Unmanned Aircraft Systems integration in the National Airspace System, or UAS in the NAS, project.

This project was a new type of undertaking that worked to identify, develop, and test the technologies and procedures that will make it possible for unmanned aircraft systems to have routine access to airspace occupied by human piloted aircraft. Since the start, the goal of this unified team was to provide vital research findings through simulations and flight tests to support the development and validation of detect and avoid and command and control technologies necessary for integrating UAS into the NAS.

That interest moved into full-scale testing and evaluation to determine how to best integrate unmanned vehicles into the national airspace and how to come up with standards moving forward. Normally, 44,000 flights safely take off and land here in the U.S., totaling more than 16 million flights per year. With the inclusion of millions of new types of unmanned aircraft, this integration needs to be seamless in order to keep the flying public safe.

Working hand-in-hand, teams collaborated to better understand how these UAS's would travel in the national airspace by using NASA-developed software in combination with flight tests. Much of this work is centered squarely on technology called detect and avoid. One of the primary safety concerns with these new systems is the inability of remote operators to see and avoid other aircraft. Because unmanned aircraft literally do not have a pilot on board, we have developed concepts allowing safe operation within the national airspace.

In order to better understand how all the systems work together, our team flew a series of tests to gather data to inform the development of minimum operational performance standards for detect and avoid alerting guidance. Over the course of this testing, we gathered an enormous amount of data allowing safe integration for unmanned aircraft into the national airspace. As unmanned aircraft are becoming more ubiquitous in our world - safety, reliability, and proven research must coexist.

Every day new use case scenarios and research opportunities arise based around the hard work accomplished by this incredible workforce. Only time will tell how these new technologies and innovations will shape our world.

Want to learn the many ways that NASA is with you when you fly? Visit nasa.gov/aeronautics.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Making the Skies Safe for Unmanned Aircraft
Unmanned Aircraft Systems (commonly known as UAS or drones) are typically a smaller aircraft that fly without an onboard pilot. Currently used for research, testing, and aerial-visual purposes, these vehicles could one day carry cargo, or even passengers, through countryside and city landscapes.

UAS are a key component of our Unmanned Aircraft Systems Integration in the National Aairspace Ssystem (UAS in the NAS) project. Our research will help develop the rules so that unmanned aircraft can safely coexist with manned aircraft in the national airspace.

We collaborate with private companies, like Navmar Applied Science Corporation (NASC), to research and test aerodynamically efficient UAS. We also work with government agencies like the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) to conduct research that will contribute to setting standards and certifications.

We are leading the nation to open a new era in air transportation called Advanced Air Mobility (AAM). AAM will enable safe, sustainable, affordable, and accessible aviation that moves people and cargo between places using a transformed air transportation system and revolutionary new aircraft.

With new cost-and-fuel efficient aircraft and technologies becoming available, UAS will provide substantial benefit to U.S. industry and the public. Such benefits include air-lifted organ transplant deliveries that arrive more quickly and safely than ever before; and search and rescue missions performed with increased speed and accuracy.

There are other benefits too, like pizza being air- dropped to your front door, and less package delivery trucks on the road. The burgeoning landscape of AAM holds many potentials – and it’s our job to help safely and sustainably map out and navigate what that future landscape looks like.
Want to learn the many ways that NASA is with you when you fly? Visit https://www.nasa.gov/aeronautics. Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
5 Ways NASA Technology is Shaping the Transportation of Tomorrow
We have always been in the transportation business, whether launching astronauts to the Moon or improving airplanes to make them fly faster and safer on less fuel. And whether directly – like more aerodynamic wings for passenger jets – or indirectly – like more comfortable driver seats in sedans – this is yet another way our innovations benefit the public.
Today, the world of transportation is on the brink of some big changes. Drones are poised to make more efficient deliveries, crop surveillance and even disaster relief efforts. Taxis may soon take to the skies as well. And self-driving cars are ever closer to reality.
As we release our latest edition of NASA Spinoff, our yearly publication that celebrates the many ways our technology helps people on Earth, let’s take a closer look at some ways we’re helping augment transportation — and keeping everyone on the roads and in the skies safe.
1. Better data for driverless navigation

If cars are going to drive themselves, they need to be able to “see” and assess the world around them, from other cars to pedestrians and bicyclists to a construction cone in the road. This is accomplished with the help of 3D cameras, or light detection and ranging (lidar), which sends out laser pulses and calculates where obstacles are by how long it takes that laser to bounce back.
But that, says engineer Farzin Amzajerdian at our Langley Research Center, is like building a 3D picture one pixel at a time. Instead, a new kind of lidar grabs a full array of pixels all at once. This “flash lidar” is faster and, because it has fewer moving parts, more reliable. It sailed through initial tests for possible use on a future Moon lander, and our partner has also sold the technology to a major car parts manufacturer, for autonomous cars.
2. Opening the airspace for drones

Air traffic control has largely been a human operation so far, with people in control towers actively directing all 50,000 or so flights daily across the United States. But add in drones, and humans won’t be able to keep up: experts estimate there will soon be millions of aircraft in flight every day.
We’re helping automate and streamline flight control, working with the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and private companies to build the new technology needed to manage the anticipated challenges. Among other advances as a result, one company has built a platform used at airports, by air traffic controllers, and by drone operators around the world to more easily file flight plans, view the airspace, get clearance in restricted areas and more.
3. Software modeling for air taxis

It may sound like something from the Jetsons, but real people are imagining the technology needed to make flying taxis a thing. And they’re probably not going to look anything like the passenger planes that we’re used to.
But when you start with a totally new design, there are all sorts of variables, including how much it will weigh. When it comes to flying, weight is a critical factor. For one thing, a heavier craft needs more fuel, but more fuel makes it even heavier. And all that weight stresses the structure, which means reinforcing it (more weight again!). Do it wrong, and all these factors cycle endlessly until you have something too heavy to get off the ground.
New software, designed with our help, generates fast and accurate weight estimates of novel aircraft designs, helping engineers figure out what works and how to make it better. Among other customers? UberElevate, which is trying to take rideshares to the skies.
4. More nimble hand controls

We’ve even played a part in improving different kinds of joysticks, for everything from planes and video games, over the years. We had to because—especially in the early days of space travel—spacesuits were pretty unwieldy under the high g forces of launch and re-entry, so we needed to develop easy-to-use hand controls.
One former astronaut, Scott Parazynski, had acquired a wealth of experience training on and using NASA joysticks for jobs like maneuvering the International Space Station’s robotic arm. He realized similar technology could have even more of an impact on Earth. Parazynski, who is also a medical doctor, envisions improving robotic surgery with the new joystick he created; in the meantime, it’s already on the market for drones, making it easier than ever to use them to record aerial video, inspect a gas pipeline or even assess damage after a hurricane.
5. Helping farmers get the full picture

The “bird’s-eye view” is an expression for a reason: flying overhead provides a perspective you just can’t get with two feet planted on the ground. For the first time ever, we are going to get that bird’s eye view on Mars, and the same expertise that got us there is also giving farmers a new way to keep track of their crops.
The Mars Helicopter is poised to hitch a ride to the Red Planet with our latest rover, Perseverance, later this year. Designing it was a challenge: because there is so little air to provide lift on Mars, we needed something incredibly light (less than four pounds!) with large rotors that spin incredibly fast (nearly 3,000 times per minute).
We teamed up with a company we’ve worked with in the past on high-altitude, solar-powered, unmanned flyers. That company had something else in the works, using the same expertise: a drone equipped with two high-res cameras to capture images of crops as it flies overhead. The data from these images tells farmers where plants are thriving and where they’re not, informing them where they might need more (or less) water or fertilizer.
You can learn more about all these innovations, and dozens more, in the 2020 edition of NASA Spinoff. Read it online or request a limited quantity print copy and we’ll mail it to you!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Is it at all possible to send a drone into a black hole and collect the data of what it’s like inside? If not, how close do you we are to possibly achieving that?